Did you know that monkeys are related to a coconut tree? In fact, all living things on Earth are related and share a fundamental structure of life called DNA. That is short for deoxyribonucleic acid, which is a large molecule that carries the information an organism needs to grow and develop.
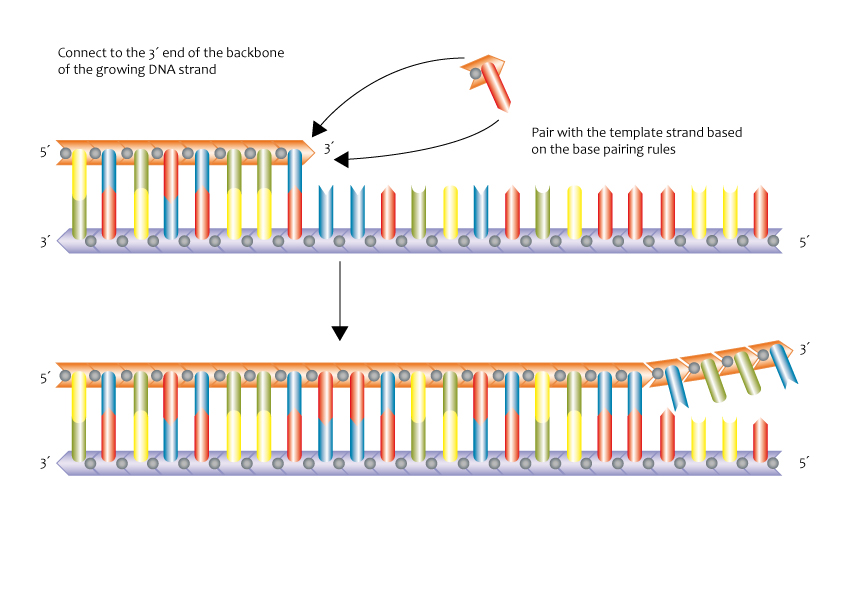
The shape of DNA is a double helix, and it looks like a spiraling ladder. Along the side of the ladder, a chain of pentose sugar, called deoxyribose, and phosphate molecules make up the backbone. The rungs of the ladder are formed by nitrogenous bases. The four bases found in DNA are adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). A single base sticks out from the backbone and forms a hydrogen bond with the base directly across it. These two bonded bases are called a base pair. Adenine always pairs with thymine, and cytosine always pairs with guanine.

Both simple one-celled organisms and multi-celled organisms, such as animals, plants, and fungi, have DNA. By comparing the DNA of two different species, scientists can estimate how closely they are related. In general, closely related species have more DNA in common than distantly related species. Organisms of the same species hardly differ in their DNA at all. Your DNA is 99.9% identical to all other humans on Earth.

Over time, small changes to DNA called mutations can occur. The more time that passes, the more mutations can happen. These mutations can result in a new species forming over time.

