Philosophers postulated the existence of an atom, although they never verified it experimentally. Atom is derived from the Greek word atomos, which means “indivisible.” The current understanding of atoms has evolved over the past two centuries of hypothesis and experimental observations.

In 1807, English schoolteacher John Dalton, postulated a theory that helped revolutionize chemistry by stating that the behavior of matter could be explained using an atomic theory. An atom is the smallest unit of an element that can participate in a chemical change. In 1807, English schoolteacher John Dalton, postulated a theory that helped revolutionize chemistry by stating that the behavior of matter could be explained using an atomic theory.
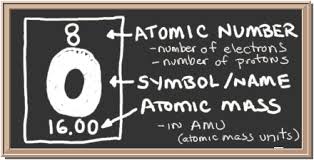
Oxygen atom has an atomic number of 8, mass number of 16, and occurs in nature as a diatomic molecule, which is two atoms occurring together as one molecule. The symbol O represents the Oxygen element in the periodic table of elements
In the late 1800s and early 1900s, the understanding of the atom further evolved based on various experiments that were conducted successfully. J.J. Thomson’s cathode ray tube experiment showed that atoms contain small, negatively charged particles called electrons. American physicist, Robert A. Millikan, via his oil drop experiment, discovered that there is a fundamental electric charge, basically the the charge of an electron. Ernest Rutherford’s gold foil experiment showed that atoms have a small, dense, positively charged nucleus. He named the positively charged particles within the nucleus as protons. English chemist Frederick Soddy demonstrated that atoms of the same element can differ in mass; these are called isotopes. In 1932, James Chadwick discovered that the nucleus also contains neutral particles called neutrons, with a mass approximately that of a proton. The existence of the neutron also explained the occurrence of isotopes.
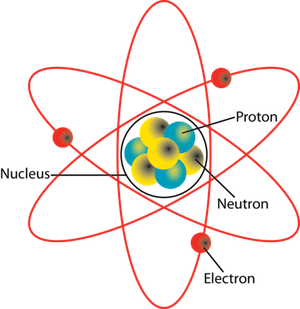
The image depicts an atom with the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom and the electrons in orbit around the nucleus.
To explain our current understanding at a high level, an atom has a central nucleus with positively charged protons and neutrons with no charge. Negatively charged electrons circle the nucleus in a cloud. Atoms can’t be seen with the naked eye but only with a special instrument called an electron microscope. Each element is made up of a different type of atom. Atoms can be combined to form substances. Elements are classified by their atomic number. The atomic number is how many protons there are in an atom. The mass number is the sum of the numbers of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of an atom.
There is usually the same number of electrons as there are protons, but not always the same number of neutrons. If an atom has a greater or fewer number of neutrons than in a regular atom, it is called an isotope. Isotopes have different atomic masses. If an atom loses or gains electrons, they are called ions. An anion is a negatively charged atom or molecule and hence contains more electrons than protons. A cation is a positively charged atom or molecule and hence contains fewer electrons than protons.