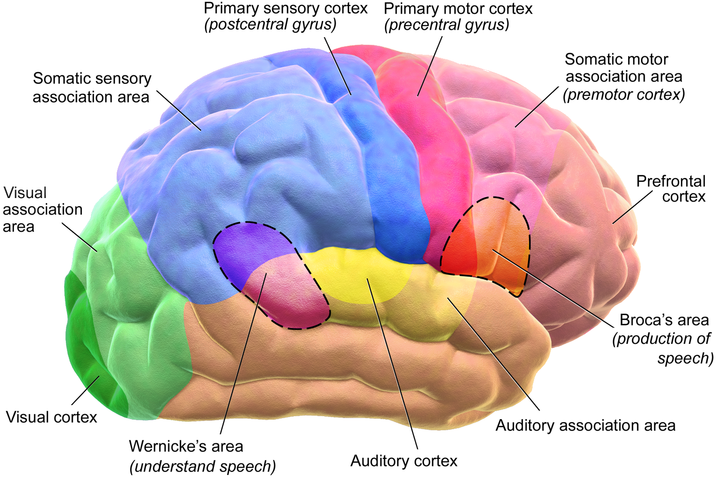
The brain consists of the cerebrum, cerebellum and the brainstem. The cerebrum is the largest part of the human brain. The cerebrum makes up 85 percent of the brain’s weight. It is divided into two cerebral hemispheres. The cerebral cortex is an outer layer of grey matter, covering the core of white matter. The cerebrum is connected by the brainstem to the spinal cord. The cerebellum lies beneath the cerebrum and has important functions in motor control. It plays a role in coordination and balance and may also have some cognitive functions. The brainstem consists of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata.
Even after a few decades of research, the human brain still remains an enigma. The human brain is estimated to have around 100 billion nerve cells. The brain itself cannot feel any pain. It simply interprets the pain signals sent to it. When the brain is starved of oxygen or glucose, It suffers irreversible damage within three to five minutes.
The brain is the fattiest organ in our body, consisting of about of 60 percent fat. A diet that is rich in healthy fats, such as omega-3s and omega-6s, is vital for brain health and overall body health as well. Twenty-five percent of the body’s cholesterol resides within the brain. Cholesterol is an integral part of every brain cell. Without adequate cholesterol, brain cells die. Our brain consists of almost 75% water. Even a 2% dehydration can affect attention, memory and other cognitive skills. It is not a myth when we hear that it is essential to hydrate and drink lots of water daily for a full functioning brain!
The human brain is the central organ of the human nervous system and, along with the spinal cord, makes up the central nervous system. It controls most of the activities of the human body. The brain processes, coordinates, and integrates information it receives from the various sense organs. It makes decisions and sends instructions to the rest of the body. The brain is protected by the skull, suspended in cerebrospinal fluid, and isolated from the bloodstream by the blood–brain barrier.

