
A Russian chemist and inventor named Dmitri Mendeleev created the arrangement of the periodic table. Scientists have discovered more elements and made the periodic table what it is today. Elements have an atomic number, chemical symbol, chemical name, and average atomic weight. The first letter of a chemical symbol is always capitalized and the rest of the other letters are lowercase. There are usually one or two letters for an element’s chemical name, but recently the newest discovered elements have been receiving temporary three-lettered chemical symbols.
Broadly, elements are categorized into metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. Each vertical column is called a group and each horizontal row is called a period. This table is called the periodic table because each element has one more electron than the one that is left to it except for the first element and the last element. Periodic means repeating. Elements in the same group have similar properties. The physical and chemical properties of elements change from one end of the period to another. The two periods that are at the bottom of the periodic table are called lanthanides and actinides. They are very rare metals and are often called inner transition metals.
The lanthanides are the elements with atomic numbers from 57 to 71. These elements are called lanthanides because they exhibit similar properties to lanthanum, the first element in the row. The actinides are elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103. These elements are called actinides because they exhibit similar properties to actinium, the first element in that row.
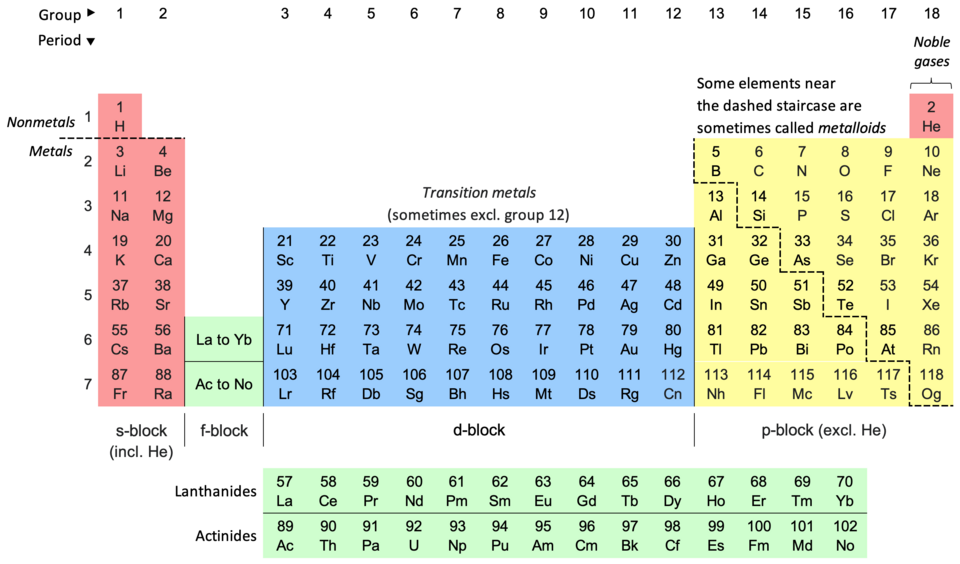
Electrons in the outermost shell of an element’s atom are called valence electrons. The number of valence electrons helps determine the kind of chemical reactions atoms can undergo. Some of the elements are very short-lived and some are radioactive. There are currently 118 elements in the periodic table right now.
